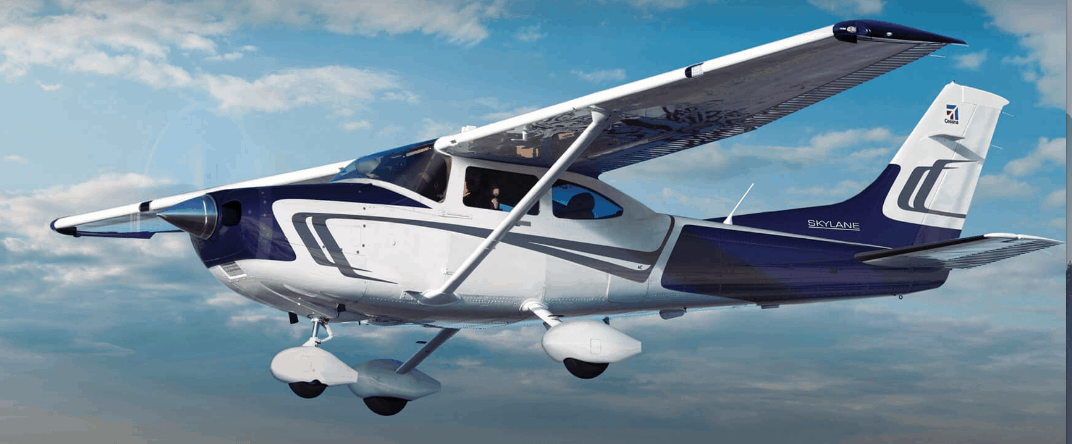
Cessna T182 Skylane
Single engine piston aircraft with fixed gear built from 1956 through 1986 before production ceased for 10 years until they were brought back into production in 1997 until current. Cessna produced a turbo-charged model from 1981 through 1986 and began production again from 2001 until 2013. The Cessna T182 Skylane seats up to 3 passengers and 1 pilot.
Specifications
Exterior Dimensions
Wing span: 36ft
Length: 29ft
Height: 9ft 4in
Interior Dimensions
Cabin Length: 11ft 2in
Cabin Width: 42in
Cabin Height: 48.5 in
Weights
Max TO weight 3100 LBS
Empty Weight: 2,017 LBS
Fuel capacity: 87 GAL
Useful Load: 1,095 LB
Engine
Manufacturer: Continental Motors
Model: TIO-540-AK1A
Horsepower: 235 HP
Overhaul (HT): 2000hr TBO allowed if new specs are met
Years before overhaul: 12
Performance Specifications for Cessna 182P and Q Models
| Horsepower: 235.00 | Gross Weight: 3,100 |
| Top Speed: 165 kts | Empty Weight: 2,017 |
| Cruise Speed: 158 kts | Fuel Capacity: 92 |
| Stall Speed (dirty): 35 kts | Range: 594 nm at 17.2 gph |
| Rate of Climb: 1,040 | Rate of Climb (One Engine): |
| Service Ceiling: 20,000 | Ceiling (One Engine): |
| Takeoff | Landing |
| Ground Roll: 775 | Ground Roll 590 |
| Takeoff Roll Over 50 ft: 1,385 | Landing Roll Over 50 ft: 1,350 |
History
The Cessna 182 was introduced in 1956 as a tricycle gear variant of the 180. In 1957, the 182A variant was introduced along with the name Skylane. As production continued, later models were improved regularly with features such as a wider fuselage, swept tailfin with rear “omni-vision” window, enlarged baggage compartment, higher gross weights, landing gear changes, etc. The “restart” aircraft built after 1996 were different in many other details including a different engine, new seating design, etc.
By mid-2013 Cessna planned to introduce the next model of the 182T, the JT-A, using the 227 hp (169 kW) SMA SR305-230 diesel engine running on Jet-A with a burn rate of 11 U.S. gallons (42 L; 9.2 imp gal) per hour and cruise at 155 kn (287 km/h). Cessna has no timeline for the JT-A and the diesel 172. The normally aspirated, avgas fueled 182 went out of production in 2012, but came back in 2015.
Development
Experience says that when a factory-turbocharged version of a popular airplane gets introduced it nearly always outsells the nonturbocharged version. It happened with the previous production 182, and it is the case with the new production Skylane; the turbo version outsells the nonturbo one by a good margin.
There are some sensible reasons for that.
First, you get a lot for the money. You could add all the elements of a turbocharged Skylane — the turbocharger, the built-in oxygen system and the heated prop — to a nonturbocharged model, but it would cost you more than Cessna charges for those upgrades (about $35,000) and you would miss out on some nice features of those systems you can't get on the aftermarket. And even if you live in the flatlands, when you go to sell your airplane, there's more of a market for the turbo version, as even Rockies dwellers will be interested in taking a look.
The airplane is faster, too, though it won't make you think you've somehow ended up in a high-wing version of Cessna's recently named Corvalis (née Columbia). The turbocharger gives you better takeoff, climb and hot and high performance, and it can maintain its mojo up to 20,000 feet, where it can make some really nice true airspeeds (up into the 170s) while stretching out the range.
The engine that powers the T182T is the Lycoming TSIO-540-AK1A, a factory turbocharged 235 engine that features an automatic wastegate and improved turbocharger cooling. The engine seems very smooth and quiet, but maybe that's because I've spent so much time in older Skylanes, where the soundproofing was very minimal.
Design
The latest additions to the airplane are few but impressive, and the list of features added when the T model was launched a few years back are numerous.
Garmin's Synthetic Vision Technology (SVT), Garmin's excellent GFC 700 autopilot and WAAS. Coupled with the G1000 system's host of other impressive capabilities, these features give the Skylane a suite of avionics utilities that are hard to beat in a single-engine airplane of any description.
The upgrades that came with the launch of the 182T in 2004 are all there, too. They include several small aerodynamic improvements — more streamlined VOR antennas, slicker wheelpants, a smaller beacon — that Cessna added in order to boost the cruise speed of the airplane by five knots or so, which does in fact seem to be the case.
The Skylane has had both WAAS and Garmin's GFC 700 autopilot for a little while now, but Garmin's SVT is brand new. In fact, the Skylane I flew in was the first production Skylane to have the system installed. It had not, however, been certified yet; hence, the “Experimental” markings on the airplane we flew. SVT should be ready to go and in new airplanes by the time you read this.
The last of the old-production Skylanes were delivered in 1986, and the new generation Skylane is a better airplane in just about every regard, the exception being weight — new production 182s are a little heavier than old models. Cessna did a much better job corrosion-proofing the airplane. The seats safer, stronger, more durable and a lot more comfortable. Cessna greatly improved the fit and finish of the interior and added state of the art avionics. The airplane is quieter, smoother and more versatile, with longer range tanks and improved aerodynamics. The new generation Cessna piston singles are extensively re-engineered airplanes that are thoroughly modern versions of the bestselling airplanes ever. So if you think that Cessna is still building the same old airplanes it did 50-odd years ago, think again.
Variants
Cessna T182 (1981-1986) sn 67716-68615
Four-seat light aircraft with fixed landing gear, powered by a turbocharged 235 hp (175 kW) Lycoming 0-540-L3C5D, piston engine, gross weight of 3,100 lb (1,406 kg) for take-off and 2,950 lb (1,338 kg) for landing. Certified on 15 August 1980.
Cessna T182T Skylane (2001-2013) sn 08002-9100
Four-seat light aircraft with fixed landing gear, powered by a turbocharged and fuel-injected 235 hp (175 kW) Lycoming TIO-540-AK1A piston engine, gross weight of 3,100 lb (1,406 kg) for take-off and 2,950 lb (1,338 kg) for landing. Certified on 23 February 2001.
Cessna T182JT-A Turbo Skylane JT-A (2013-2015)
Four-seat light aircraft with fixed landing gear, powered by a 227 hp (169 kW) SMA SR305-230 diesel engine, it burns 11 U.S. gallons (42 L; 9.2 imp gal) per hour of Jet-A fuel and cruises at 156 kn (289 km/h). The model was first flown in May 2013, and as of July 2015, FAA certification is on hold indefinitely. Originally introduced as the Turbo Skylane NXT, Cessna changed the name to avoid confusion with the Remos NXT.
Click here to view Performance Specifications for each Model