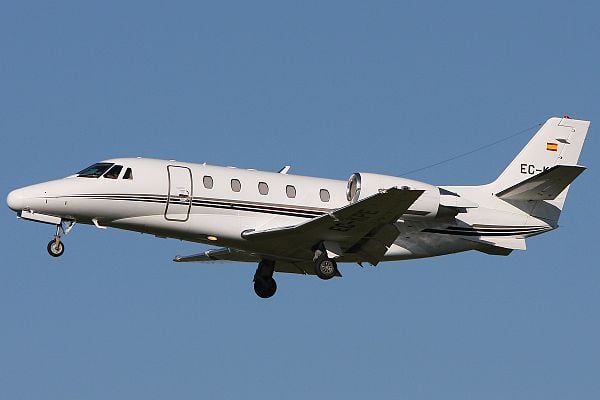
Cessna Citation Excel
The Cessna Citation Excel model 560XL series is a midsize business jet produced by Cessna from 1998 until 2003. The Citation Excel had the cruciform tail and unswept wing of the Citation V and the stand-up cabin of the Citation X but slightly shortened. The Excel has the roomiest cabin in its class of light corporate jets and can seat up to 10 passengers (in high-density configuration; typically the number is six to eight in a corporate configuration), while being flown by a crew of two.
Specifications
Exterior Dimensions
Wing span: 55 ft 8 in
Length: 52 ft 9 in
Height: 17 ft 2 in
Interior
Cabin height: 5 ft 8 in
Cabin width: 5 ft 5 in
Cabin Length: 18 ft 7 in
Baggage volume: 79 cu.ft.
Seating: typically configured for 8 passengers 2 crew
Avionics
Honeywell Primus 1000 avionics, Dual FMS, XLS+ includes ProLine 21, TAWS B, RVSM, TCAS II, APU.
Engines
Manufacturer: Pratt & Whitney
Model: pw500
Horsepower: 3,650–4,080 lbf
Performance
| Horsepower: 4080.00 | MTOW: 20,000 |
| Top Speed: 433 | Empty Weight: 12,800 |
| Cruise Speed: 423 | Fuel Capacity: 6740 |
| Stall Speed (dirty): 97 | Range: 2100 nm |
| Rate of Climb: 3790 fpm | Rate of Climb (One Engine): 699 |
| Service Ceiling: 45,000 | Ceiling (One Engine): |
| Takeoff | Landing |
| Ground Roll: 3590 ft | Ground Roll: 2909 |
| Takeoff Roll Over 50 ft: | Landing Roll Over 50 ft: |
History
The Cessna Citation Excel is an American midsize business jet built by Cessna. Announced in October 1994, the Model 560XL first flew on February 29, 1996, certification was granted in April 1998 and 1000 have been delivered. The 2,100 nmi-range (3,900 km), 20,200 lb (9,200 kg) MTOW jet is powered by two 3,650–4,080 lbf (16.2–18.1 kN) PW500 turbofans, has the Citation V (560) cruciform tail and unswept supercritical wing of 370 sq ft (34 m²), and the Citation X stand-up cabin slightly shortened.
Development
With the success of Cessna's high-end Citation VII, the manufacturer saw a market for an aircraft with the Citation X's features but aimed at a more traditional market, where it would chiefly compete with twin-turboprop aircraft.
The project was announced at the annual NBAA convention in October, 1994, and the prototype aircraft took off on its first flight on February 29, 1996. Federal Aviation Administration certification was granted in April 1998, by which time Cessna had over 200 orders for the aircraft. Its unit cost in 1999 was US$8.7M. By the time the 100th Excel was delivered in August 2000, an aircraft was coming off the Wichita production line every three days. A total of 308 were built before production switched to the Citation XLS.
Design
Rather than being a direct variant of another Citation airframe, the Excel was a combination of technologies and designs. To produce the Excel, Cessna took the X's wide, stand-up cabin fuselage, shortened it by about 2 feet (0.61 m) and mated it with an unswept wing utilizing a supercritical airfoil (based on the Citation V Ultra's wing) and the tail from the Citation V. The Excel has the roomiest cabin in its class of light corporate jets and can seat up to 10 passengers (in high-density configuration; typically the number is six to eight in a corporate configuration), while being flown by a crew of two.
To power the aircraft, Cessna chose the Pratt & Whitney Canada PW500 turbofan. The original version had two cockpit configurations involving where the landing gear was on the panel. With the gear on the left hand side, the MFD was moved to the right slightly and both radios were moved to the right of the MFD next to each other. With the gear handle on the right side, the MFD remained centered with the radios on either side. The Excel uses Honeywell avionics and an optional Auxiliary power unit also powered by Honeywell.